We never like not to have that score appear on our tests. Neither was on the scoreboard when we were cheering for our favorite team. However, we want to see a couple of them put after any figure from 1-9 for the money we have in our bank account.
That is the mystery behind the number 0—an intriguing number, even though its existence is sometimes taken for granted.
The value of zero is above and beyond that of any other number. The idea of zero and its symbolism may be profound and peculiar simultaneously, which helps you comprehend the significance of zero in mathematics.
It’s not surprising that we understand the importance of numbers in our lives, but we don’t understand the worth of zero unexpectedly. Many have asked ourselves, “Is zero even a number?” To provide an appropriate response to that question, we must first acquire an understanding of the number zero.
We can distinguish between 1 or 15, or 256. There are 256 pupils in the classroom and 15 automobiles in the parking lot, but to comprehend the number 0, we need to realize something is missing. For example, we need to understand that there are no cars on the road or birds in the sky.
The following is a remark from Robert Kaplan, a professor of mathematics at Harvard and the author of a book on zero. In it, he discusses the symbolism of zero and says, “Zero is in your head, however, not in the sensory world.”
Invention of Zero

No individual can be given credit for ‘creating’ the zero. Around five thousand years ago, the Sumerians used a positional system that did not include the digit 0. To differentiate between numbers such as 104 and 10004, for instance, a symbol or a space was used in place of the digit 0. They placed a slanted double wedge between each pair of cuneiform symbols representing numerals. On the other hand, this sign was never appended to the end of a numerical value. The Sumerians unmistakably anticipated that you would deduce that information based on the context.
The term “zero” comes from the Hindi word “sunyata,” which means “nothingness” and is an essential idea in Buddhism. The word “zero” was initially taken from “sunyata.”
Indian mathematician and astronomer Brahmagupta is credited with being the first to define the number zero and its operations and devise a symbol for it. [1]
The ancient Mayans of Central America are credited with inventing the unique zero in their system of numbers. The number zero, which serves as a placeholder, was separately developed by many worldwide civilizations.
The Arabs were the ones who first warned people in the Middle East about Zero. The zero then started on its adventurous voyage to Europe from that location. The mathematician Fibonacci became fascinated with this number in the 1200s, and as a result, he was the one who popularized the “Arabic” numeric system that we continue to use today.
So, the question of who first used the zero has been answered. It isn’t easy to comprehend that all of the endless methods in mathematics revolve around the concept of zero as their pivot point.
Evaluation of Zero from the Beginning
The Western philosophical tradition has a pessimistic perspective on the idea of nothing, yet, the introduction of the number zero brought about a significant reduction in the complexity of mathematical calculations. It allowed mathematicians to develop fundamental mathematical disciplines such as algebra and calculus. When we realize that this notion enhanced the computing process and prepared mathematicians in historical periods to tackle more intricate issues, we can see the significance of zero. Consequently, they could investigate the general characteristics of numbers and advance mathematics.
- Mathematically speaking, the zero condition is essential since it serves as the additive identity of real numbers and integers. In addition, the number zero is a critical factor for algebraic structures. Zero plays a significant role in the place value system because of its role as a placeholder.
- A further realization of the significance of zero in mathematics comes about when considering fractions. If it weren’t for zero, we probably wouldn’t be studying particles in school. Additionally, the intriguing zero led to the development of a more precise method for describing fractions. For instance, we now know that adding zeros to the end of a number enhances its value and effect, but adding zeros to the beginning of a number, with the assistance of a decimal point, diminishes the magnitude of the number. This can be shown by looking at an example.
- How could we possibly have negative numbers if there were no such entity as zero? Confused? You can see that zero does not qualify as either a positive or negative integer. It defines the line that separates positive and negative integers. As a result, the initial value on many scales is zero. Understanding and elucidating ideas that do not have material manifestations are made more accessible by zero.
- The value zero is used as a stand-in for other values in the place value system. A position in the hundreds is indicated by writing two zeros before a number, while a place in the tens is marked by writing a single zero before a digit.
- Also, one must not forget that the number zero served as the foundation for the binary system used in computers.
- Zero is essential to the functioning of all digital systems today. To express ideas, the computer can understand binary language, which only has two digits—0 and 1—. Therefore, the omnipresent zero was necessary for the dawn of the digital era. Consequently, it can be shown that the need for zero is present in our day-to-day existence.
Importance of Zero
Find out how it got to be such an essential part of our lives by working together:
Utilization in Thermometer Applications
When calculating the temperature of the human body, zero is a necessary reference point. Shallow temperatures are portrayed with the assistance of negative numbers, while on the right side, positive counterparts help in the assessment process. The left side of the graph contains a sequence of negative numbers, while the right has its positive equivalents.
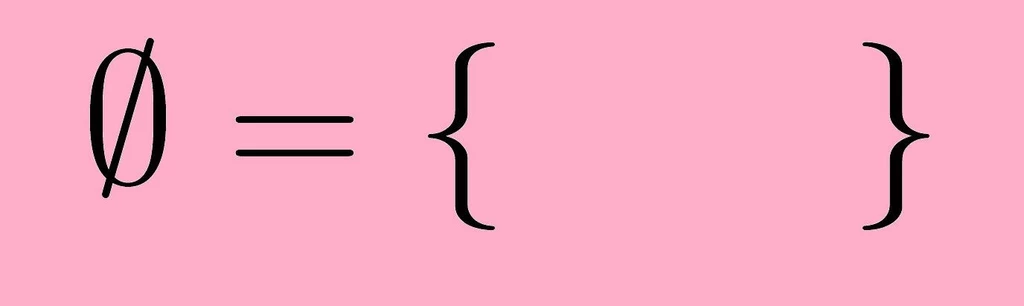
Representation of an Empty Set
Only with the assistance of the zero number is it feasible to represent an empty set that does not include any items. Calculations, which were before impossible, have been made much simpler for the mathematician due to this development. Because there is a zero in the number system, mathematical judgments must adhere to a predetermined set of criteria. Users have reported that it has assisted them in efficiently arriving at correct findings.
For instance, according to the rule, adding or subtracting zero from the number will not change the result’s significance. In addition, the number would be equal to zero if it were to be removed from itself using the whole number.
Exciting Characteristic of Division
When divided by zero, any integer produces zero results, whereas any other number produces an uncertain amount when divided by zero. This feature of zero, known as its “division property,” is highly fascinating. Calculations in algebra and mathematics may benefit significantly from their use.
Exponents
There is a connection between the number of zeros in a number and the order of the exponents in the power of 10. In the form of an exponential, the number 2000, for instance, may be written as 2 times 10 to the third. Finding the exponents by counting the zeros in the expression is feasible.
Rounding Off the Values

In rounding out the figures, zero plays a vital role as well. If the digits that come after the decimal point are more prominent than or equal to 5, it is changed to 0, and the digit that comes before the decimal is given an increment of 1 value.
Adding Correct Amounts of Weight to Each of the Digits
The zero is the sole digit in the number that may be used to establish the place value of the other digits. However, leading zeros do not impart place value to the digits themselves; for example, the hundreds position is indicated by two zeros before the digit, whereas the tens position is shown by a single zero before the number.
It is unbearable to explain the idea of a null set without first introducing the number zero. Zero has also played a significant role in developing many physical quantities that are now an integral element of the scientific method. Since its conception, the number has emerged as the focal point of interest for mathematicians, and it is predicted that this drift will continue into the foreseeable future.
Conclusion
The significance of the number zero has not diminished for many centuries. The importance of the number zero in our lives, even though it represents nothing, has been summed up by a saying attributed to an unknown author: “Zero is meant to be nothing, yet works marvels if on the correct side.”
Contact Edulyte if you are interested in learning more about the management of mathematical computations and ideas, which naturally entails the number zero. Not only do our teachers develop strategies to assist you in becoming proficient in mathematics, but they also make the educational process enjoyable.
