Archimedes, also regarded as the “Father of Mathematics,” made many contributions to math. Not only did he have important influences on the discipline of mathematics, but he also made substantial contributions to the field of physics.
He was also an astronomer and made several significant contributions to the science of astronomy and a mathematician. Over his long life, which spanned 75 years, he established various mathematical principles and hypotheses. [1]
With the assistance of applicable laws, theorems, and formulae, all of us can measure the area and volume of various forms. However, we do not know where these laws and procedures originated from in the past. Archimedes could calculate the area and volume of various 3D and 2D forms.
We are unable to consider mathematics without him and the contributions he made. Many more of his innovations came into existence, all of which we should acknowledge.
Archimedes’ Principles
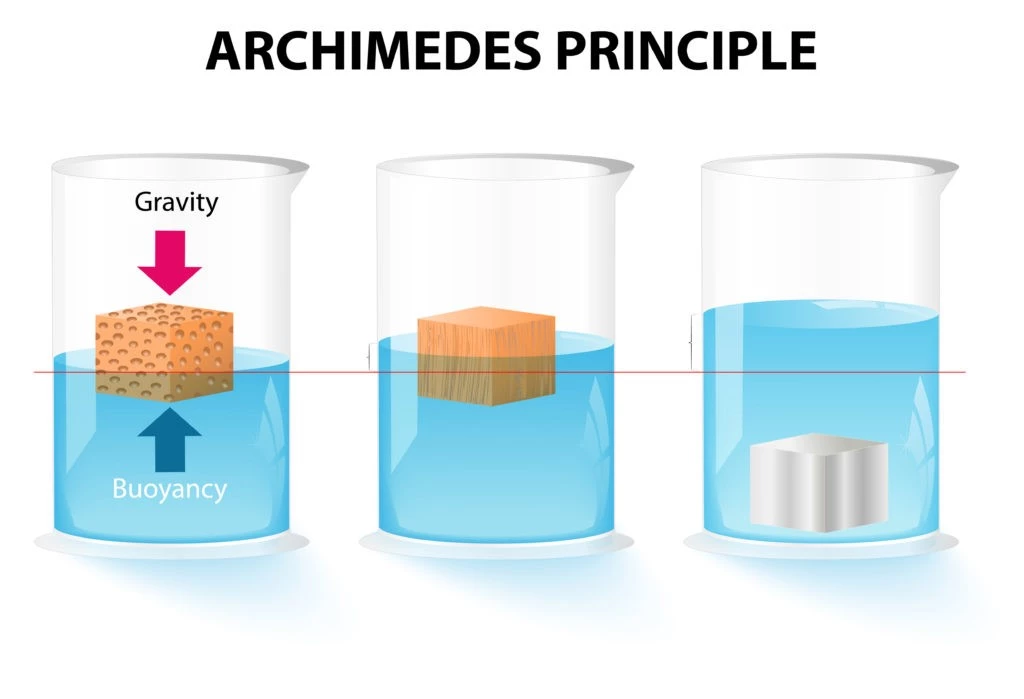
The Archimedes principle is a theory that is fundamentally about buoyancy, even though many of us find it challenging to get our heads around this idea.
When a solid object is dropped into a liquid, it displaces a quantity of fluid relative to the volume of the solid object submerged in the liquid. A body in any drink is subjected to the influence of several different forces.
Because it demonstrates that the quantity of liquid displaced is the measure of the sinking or rising capacity of the item, Archimedes’ principle also assists us in comprehending the factors that determine whether something floats or sinks. The amount of liquid taken up by the thing determines whether it will float or sink.
This law has been beneficial in comprehending the maritime concepts employed by ships and submarines, which are all constructed utilizing the idea of buoyancy. The lactometer, an instrument used to assess the purity of milk, is likewise based on the idea just discussed.
The Sand Reckoner
Imagine trying to tally up individual grains of sand. This is the goal that Archimedes set for himself. In his work titled “The Sand Reckoner,” Archimedes makes an effort to calculate the number of sand grains necessary to cover the whole of the cosmos.
First, Archimedes needed to figure out how to count a number with a massive base, leading to his significant mathematics advancement. Until then, the Greeks had used various symbols to symbolize their numerical system.
In mathematics, Archimedes developed a new theory that could count numbers up to an infinite value. The most significant number that has ever been counted is eight times 1063, as seen in Archimedes’ Sand Reckoner, in which he calculated that it would take eight times 1063 grains of sand to cover the whole cosmos.
Evolution of Pi

Mathematically, Archimedes was a practitioner of the Hellenistic technique. Because of his extraordinary intelligence, Archimedes calculated the value of the Greek symbol “Pi,” which is used in various mathematical formulas.
The value of pi, expressed as a number, is about 3.14 and may be arrived at simply by dividing 22 by 7. Pi is the ratio calculated by taking a circle’s circumference and dividing it by its diameter.
Archimedes was also responsible for drawing a variety of forms inside the circle. In mathematics, the concept of Pi has been used in various contexts, including calculating the area of a process. The size of a hemisphere can be calculated using pi, but it can also be used to compute the size of a sphere.
The Claw of Archimedes
Archimedes was born in the seaside city of Syracuse, which was located in what is now Italy but was part of Greece at the time. Archimedes devised a hook that, if attached to an opposing vessel, would cause it to capsize and sink to defend the city from attack. This was often referred to as “the iron hand” or “the claw of Archimedes.”
He was a scientist and an architect, and the Claw of Archimedes was a remarkable feat of architecture that helped the inhabitants of Syracuse to protect themselves against Roman invasion by sea. Archimedes was an architect. Because Archimedes had considered the water’s buoyancy, the claw could flip a warship over.
Archimedes’ Screw
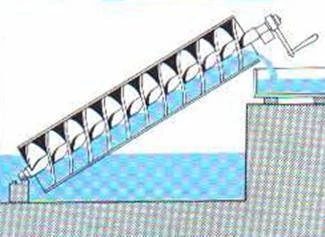
The screw invented by Archimedes was more of a pump than a screw. It worked by pumping water upward against the force of gravity. It was vital in assisting farmers in irrigating their properties, and the screw could be spun by any physical method, such as manually or by wind using a windmill.
Working against the force of gravity, Archimedes’ screw made it possible to transport water from a lower to a higher level effortlessly. This was previously a challenging task.
Today, the Archimedes screw may be found in various applications, including plastic reforming machines, die-casting machines, and molding machines, to name a few. The rapidly revolving screws utilized to assist pump water are also helpful for generating energy in a separate application.
This method is still used in many of the world’s developed nations for the watering of crops as well as the generation of energy utilizing spinning turbines. The United States of America has built a hydroelectric plant that uses a reverse screw, and this screw may also be used to drain water from low-lying regions during floods.
Archimedes’ Death Ray
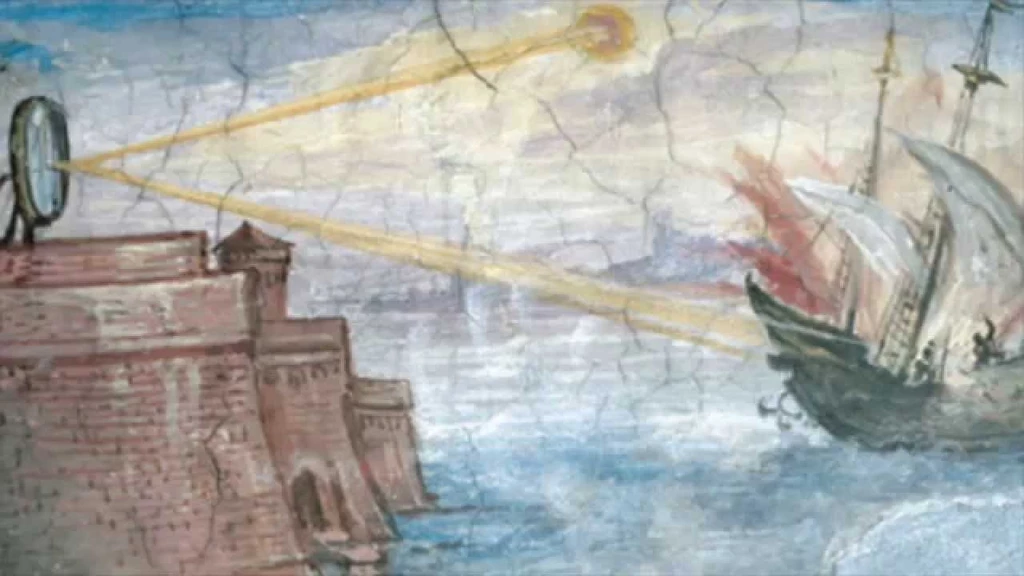

There is no room for debate on Archimedes’ status as a brilliant inventor; the death ray is not an exception to this rule. This parabolic mirrored structure was designed to focus sunlight over a specific ship location, which would then catch fire, eventually leading to the boat going down.
The idea was revisited to create a protective system for Syracuse. They were successful in their mission to destroy the nameless Roman army by setting fire to the enemy ships.
Because the boats are constantly moving, some researchers believe this method is unsuccessful; nevertheless, a few years ago, a Greek scientist named Dr. Ionnais Sakkas demonstrated that this idea is correct.
Sakkas was able to reproduce the idea by employing historical data and information. He guided 70 mirrors held by 70 guys in the direction of a boat that was 160 feet distant. He set up the mirrors. Very quickly, the ship started to catch fire.
Volumes and Areas
Because of his deep and abiding passion for mathematics, he was the first to develop formulas for calculating the volume and area of a variety of new forms by using the exhaustion approach and basing his calculations on the shapes he already knew. For instance, to determine the total area of a circle, he began by enclosing the process inside a polygon and then proceeded to create more polygons inside that circle. [2]
After that, he attempted to compute the total area covered by the drawn polygons. He then tried the same process with other forms, such as enclosing the circle inside a triangle, square, or pentagon, along with different shapes that he was familiar with.
He made several educated guesses about the area of these forms before arriving at a conclusion that provided him with the circle’s location. The name for this approach is the “Exhaustion technique.”
Infinitesimal
Archimedes is credited with being the first to develop integral calculus, meaning he did it around 2000 years before Newton and Leibniz. A quantity is said to be infinitesimal if it goes toward infinity, which denotes that it leans toward something that does not typically exist or is unreal.
As a result of the development of this notion, several other related concepts, including continuity, differentiability, limitations, and integration, came into being.
Sphere and Cylinder
Archimedes was the first to discover the relationship between the volume and the surface area of a cylinder and a globe. Because he established a relationship between a cylinder and a sphere (enclosed in a cylinder) having the same height and diameter, this is considered one of Archimedes’s most important contributions to the field of mathematics.
Archimedes believed it was his most valuable contribution to this study area. He demonstrated that the volume of a sphere and its surface area is 2/3rds that of a cylinder.
Because of this realization’s profound impact on him, he ordered that his tomb be constructed as a cylinder containing a sphere that was enclosed inside it.
The Volume Of Irregular Objects
The epiphany that led Archimedes to discover the principle of buoyancy is widely regarded as one of the most vital discoveries ever made in physics. This discovery earned Archimedes the nickname “Eureka.”
He successfully determined the volume of irregular objects by using buoyancy as a tool in his calculations. One day, he stepped into a bathtub full of water to the rim. When he entered the room, he saw that part of the water in the tub had moved due to his presence.
At that point, he had the epiphany that the volume of the body, when submerged in water, is equivalent to the amount of water it pushes out of the way and that this can be computed.
Spiral
It is a coil antenna built to have consistent spacing between the lock turns. It finds procedures in various industries, including the military sector, where it helps cover a broad spectrum of radio frequencies; GPS also uses it.
Catapult
As was just said, he used his understanding of geometry by constructing various weapons to protect Syracuse’s people from their adversaries. One of these weapons was a catapult, which functions according to the concept of a projectile.
Stone thrower is another name for this item. The mechanism of the catapult consists of a beam coupled to a pouch serving as the storage location for the projectile. Then, a hefty weight is connected to the other side of the shaft.
When released, this weight will project the stone stored in the pouch to a great distance, where it is capable of causing a great deal of harm. Initially, the beam was first hauled by hand rather than being assisted by large weights.
Final Words
Archimedes was a very significant and influential figure. He was a great patriot and a well-known mathematician, inventor, scientist, and philosopher. He also worked in the field of science. In ancient Greece’s history, Archimedes represents both the Classical and the Hellenistic periods. He was killed while employing mathematical calculations and scientific experiments to defend his city, Syracuse, against the Romans.
The innovations of Archimedes have had a significant influence on our day-to-day lives and have made things simpler. Great philosophers tend to give rise to even better philosophies and vice versa.
People are motivated to seek their particular skills and are encouraged by a well-known saying attributed to Archimedes. The quote encourages individuals to pursue their talents and states, “Give me a place to stand, and I shall move the globe.”
Archimedes was an example of an ancient Greek who was a mathematician and philosopher and provided the world with some of its finest innovations. The ancient Greeks were extensively engaged in the arts and culture of their day.
