Any solid object with three unique dimensions is considered to have three dimensions, making it a 3-dimensional form (length, width, and height). Adding a third dimension causes these designs to occupy much more space than just two dimensions.
This indicates that two-dimensional objects do not have the thickness or depth that three-dimensional ones possess. Observing the space that 3D forms occupy is another method for determining their identities. 3D shapes can’t occupy the same volume as 2D ones.
For example, piling two boxes on top of each other would require using two distinct locations. On the other hand, if an infinite number of two-dimensional squares were placed on top of each other, they would not take up more space since they would all be in the same place.
Solids are considered three-dimensional forms since they have length, breadth (width), and height dimensions. The term “three-dimensional” may be found in the phrase “3D forms.”
Every three-dimensional geometric form takes up some space because of its dimensions, and we encounter many different kinds of three-dimensional shapes in our day-to-day lives. The cube, the cuboid, the cone, and the cylinder are all instances of three-dimensional forms.
Characteristics of Three-Dimensional Shapes
A three-dimensional figure is defined by its face, edge, and vertex. These three components make up the figure.
The term “face” refers to any one of the figure’s surfaces, regardless of whether it is flat or curved. Moreover, the line that separates two sides of a three-dimensional form is known as the edge of the figure.
The point at which three of the faces of a three-dimensional form meet is known as the vertex of the figure. The word “vertex” may also be written as “vertices.”
Various Forms Of 3D Shapes
Sphere

The form of a sphere may be described as round. It is a three-dimensional geometric form with all the points on its surface equal distances from the shape’s center. Even though it seems spherical, our planet Earth is not a sphere.
Our planet has the form of a spheroid, as seen from space. Spheroids are similar in appearance to spheres; however, unlike spheres, the radius of a spheroid varies from its center to its surface at different places. [1]
It has the form of a ball and is symmetrical throughout its surface. It is possible to calculate its volume as well as its surface area, as well as its radius, and diameter. Every point on the sphere’s surface is located the same distance from the center.
It just has one face, and it does not have any edges or vertices. Because it has no flat faces, it cannot be considered a polyhedron.
Cylinder
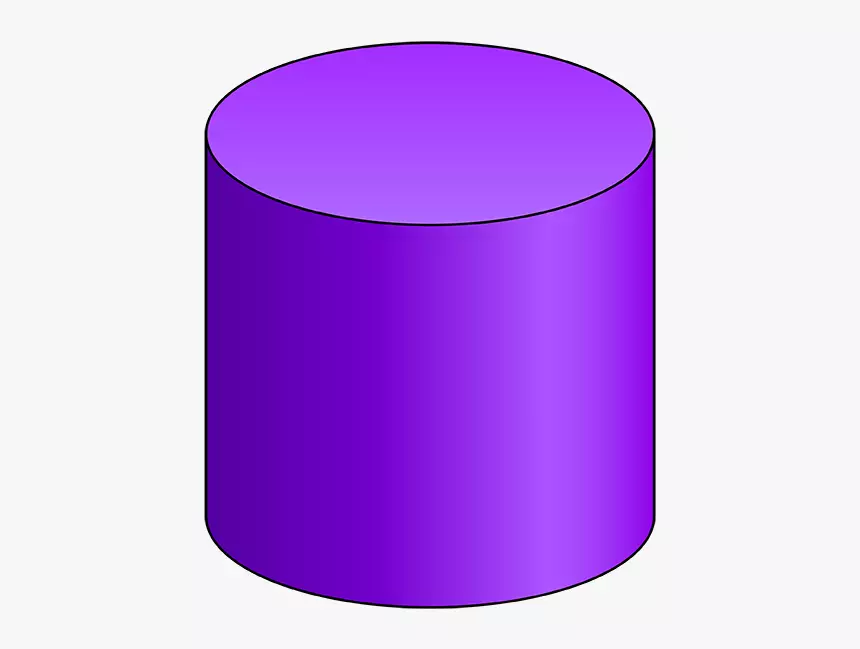
A cylinder is a three-dimensional object characterized by having one curving surface, two circular faces, i.e., one at the top and one at the bottom, and two round faces at opposite ends. A cylinder may be described by both its height and its radius. A cylinder’s size equals the distance between the top and bottom faces measured perpendicularly.
It just has one curved face. The form is consistent from the bottom to the very top. It is a three-dimensional object with two ends that are either round or oval and identical.
A cylinder is supposed to be right when its circular bases sit on the same line since this indicates that the cylinder has been constructed correctly. A slanting cylinder is one in which one of the bases is positioned at a position that is offset from the other bases.
Cube and Cuboid
The cube and the cuboid are examples of three-dimensional objects known as 3D shapes with similar characteristics in terms of the number of faces, vertices, and edges. A cube has six square faces, and a cuboid has six rectangular faces—the primary difference between the two types of three-dimensional shapes is cubes and cuboids.
The volume a cube occupies and it’s surface area is not the same for a cuboid and a cube. The length, breadth, and height are all the same in a cube, but in a cuboid, they are all different. A cube has the exact dimensions of a cuboid.
Cone
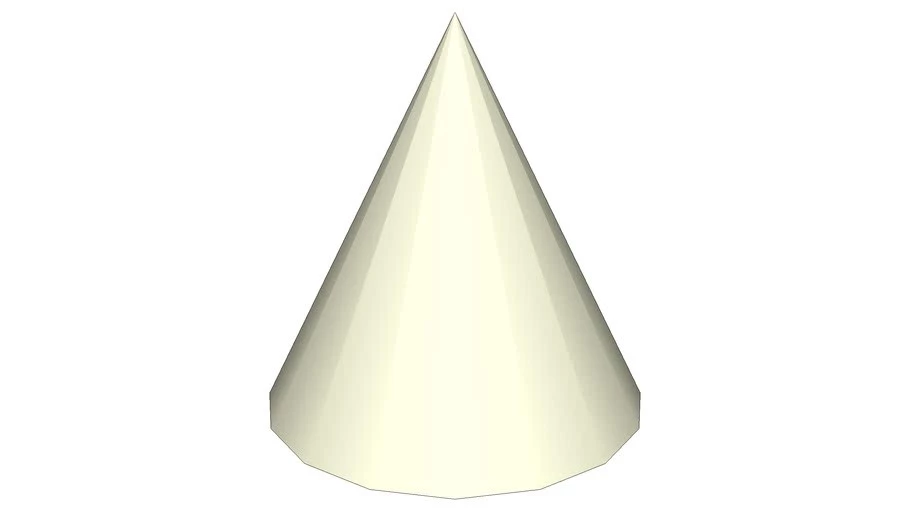

Another three-dimensional form known as a 3D shape, a cone, is characterized by a circular base that tapers out into a point at the top of the condition. “Apex” refers to the sharp point at the top of the cone. A curved surface may also be seen on a cone. Much like a cylinder, a cone may be divided into two distinct categories: a right circular cone and an oblique cone.
A cone may have a base that is either round or oval and always has an apex (vertex). A cone is just a triangle with its angles rotated.
It is possible to construct either a right cone or an oblique cone depending on the apex’s orientation concerning the base’s center.
A right circular cone is a kind of cone in which the pointy tip, also known as the apex, is perpendicular to the base of the cone. An oblique cone is a cone in which the point of the cone perpendicular to the bottom is, where the apex is located.
A cone is defined by both its height and its radius. In addition to its size, a cone also has a slant height, the distance between the point where the cone’s apex meets its circular base and any other point on the base’s circle.
Torus
A torus is a form that exists in three dimensions. In the space of three sizes, it is produced by rotating a smaller circle with a smaller radius, denoted by r, around a larger circle with a greater radius, represented by R. [2]
A torus is a continuous ring that looks like a doughnut or a tire. It does not contain any edges or vertices at all.
Pyramid
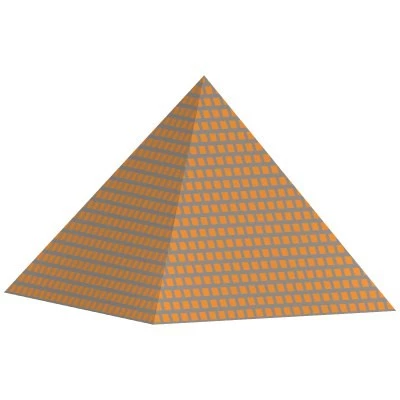
It is a polyhedron with a sordid in the shape of a polygon and an apex with parallel edges and flat faces. It is possible to divide them into regular and oblique pyramids according to the orientation of their heights about the center of the base.
The Tetrahedron is a name given to a pyramid with a base in the shape of a triangle. The term “square pyramid” refers to a pyramid that has a base that is of a quadrilateral shape. Also, it refers to a pyramid with the base shape of a pentagon. Moreover, it relates to a kind of pyramid with the base of a regular hexagon.
Polyhedron
A polyhedron is a three-dimensional form that contains polygonal faces (such as triangles, squares, and hexagons) with straight edges and vertices. A platonic solid is another name for this thing. Five polyhedrons are regular in shape. A regular polyhedron is one in which each face is identical to the others. For illustration purposes, the beginnings of a cube are all in the form of a square.
Prisms
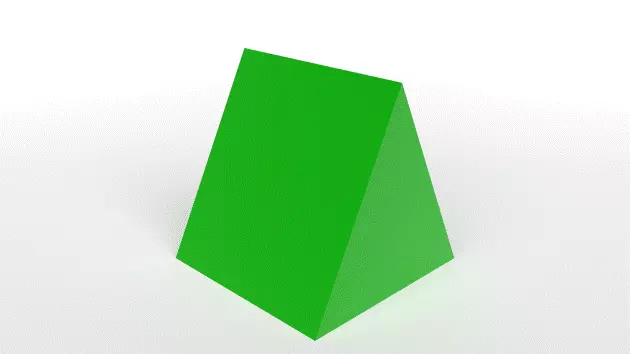
Prisms are solids that have ends that are identically shaped polygons and sides that are flat parallelograms. Along its entire length, there is no change in the cross-sectional shape.
Prisms come in various shapes, including triangles, squares, pentagonal, and so on. Prisms may also be categorized as either regular or oblique, depending on their orientation.
