There are primarily three different fractions in mathematics: mixed, improper, and proper. Returns are considered fractions if they contain both a numerator and a denominator. Explain the many kinds of fractions in terms of these two key concepts, which are referred to as the numerator and the denominator. Particles are used to dissect entire objects into their component pieces. For example, we split a pizza into four parts. Each slice of pizza is equal to one-quarter of the whole. In this instance, one is considered to be the numerator, while four is considered to be the denominator.
A fraction may be defined as the relationship between two integers in its most fundamental form. The number at the top of a fraction is referred to as the numerator, while the value at the bottom is referred to as the denominator. When anything entire or complete is cut into a certain number of pieces, each is regarded as a fraction of the original whole.
Therefore, there are a total of six different types of fractions. These are called equivalent fractions, like fractions, fractions, improper fractions, and mixed fractions.
Types of Fractions
The following are six types of fractions in mathematics:
- Proper fraction
- Improper fraction
- Mixed Fraction
- Like Fractions
- Unlike Fractions
- Equivalent Fractions
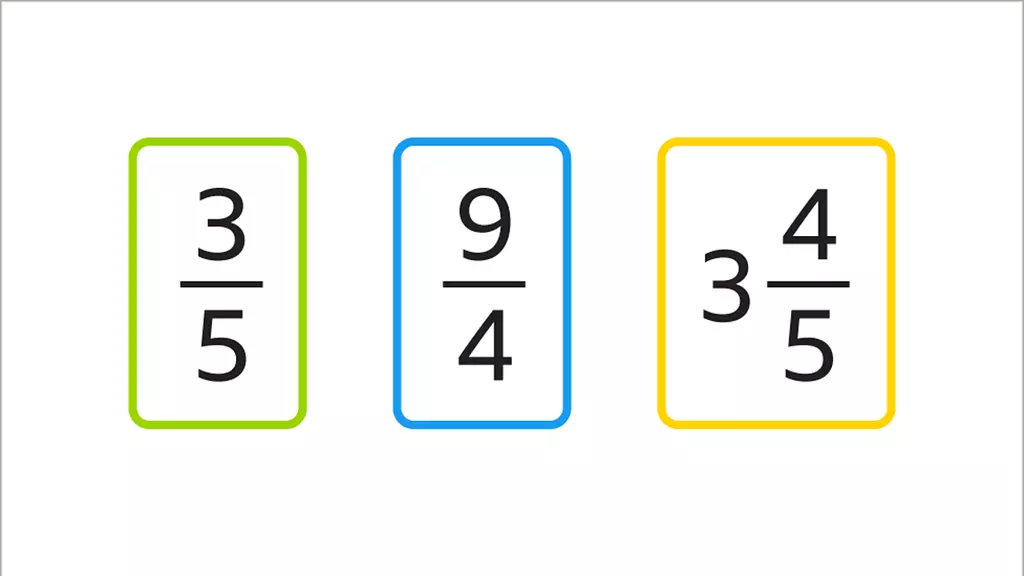
Proper Fraction
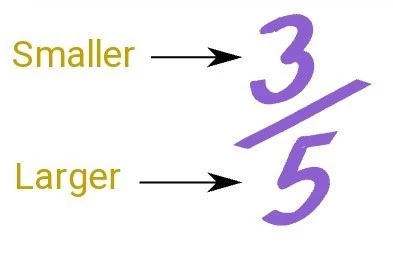
A proper fraction is a fraction in which the fraction’s numerator is less than the fraction’s denominator; further, the numerator is smaller than the fraction’s denominator. When broken down even further, the value of a valid fraction is always less than 1.
For instance, the fraction 7/5 is an illustration. The numerator of this fraction is 7, whereas the denominator is 5, as seen above. It is plain to see that the numerator of this fraction, which is 7 multiplied by 5, is greater than the denominator. As a result, it is an accurate fraction.
Improper Fraction
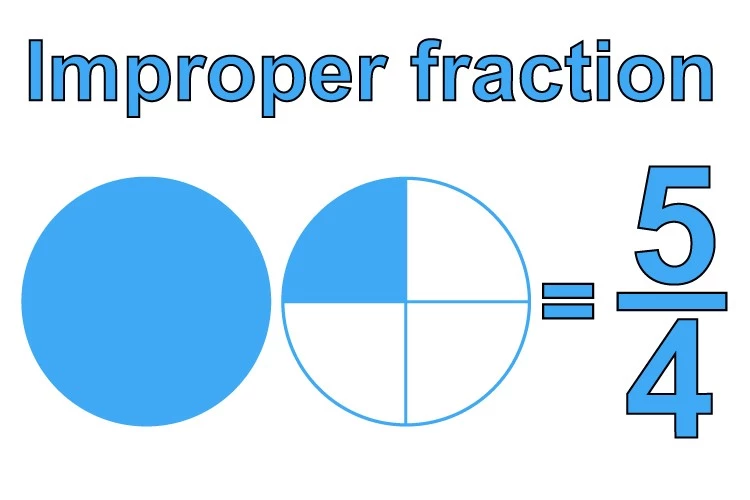
An improper fraction is in which the fraction’s numerator is more than the fraction’s denominator. Put another way; the numerator is more significant than the denominator. Because the numerator and denominator are always equal, we can express all natural numbers using fractions.
If we simplify the improper fraction, we will always have a number equal to or higher than one but never a value less than 1. Take, for instance, the fraction 8/5 as an illustration. Eight is the value of the numerator, and five is the value of the denominator in this fraction.
It is plain to see that the numerator in this fraction is more significant than the denominator, which means that eight is more than 5. As a result, it cannot be considered a valid fraction.
Mixed Fraction
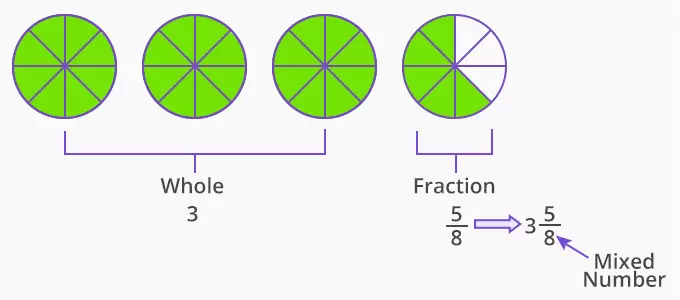
The fraction containing a mixture of a natural number and another fraction is called a mixed fraction. In its most basic condition, it is an incorrect fraction. One of its many benefits is that a mixed fraction may permanently be transformed into a fraction.
An incorrect fraction may be changed into a mixed fraction in certain circumstances. When mixed, the result will always be a number larger than one.
Like Fraction
Like Fractions are the types of fractions with the same denominator since this makes them easier to compare. The fractions 1/2, 5/2, 7/2, and 3/2 are all examples of like fractions.
Since the denominators of both fractions are identical, simplifying similar fractions is a fairly straightforward process for us. To add similar particles, we must first add up all the numerators and divide that total value by the denominator, which is the same for each particle. The formula for accomplishing the same goal is as follows: 1/2 plus 5/2 plus 7/2 plus 3/2 = (1 + 5 + 7 + 3)/2 = 16/2 = 8
Unlike Fraction
In contrast to other fractions, unlike fractions have denominators that are either uneven or distinct from one another. The fractions 1/2, 1/4, 1/3, and 1/5 are all examples of, unlike fractions. To simplify dissimilar fractions, we must first factorize the denominators, and then we may go on to facilitate the particles themselves. As a result, it needs to go through a laborious process.
For instance, we need to add a half and a quarter together. Then, given that this is the circumstance, the first object that we need to do is locate the LCM of 2 and 4, which is equal to 4. Once we have determined the Least Common Multiple of the denominators, we will need to multiply 1/2 by 4 and 1/4 by 2 in both the numerator and the denominator.
The fractions will be rewritten as 4/8 and 2/8 at that point. Now, if we take 4/8 and add it to 2/8, we get 6/8 as the final result.
Equivalent Fraction
After simplification, if two or more fractions have the same conclusion, meaning that they are expressing the same piece of the total, those fractions are referred to as equivalent to one another and have the same value.
One example of an analogous fraction is the relationship between the fractions 12 and 2/4 and 1/3 and 3/9.
How to Resolve any Fraction
If you grasp the fundamental premise, solving fractions is a straightforward process. To begin, you need to have a firm grasp that you can only execute operations such as adding and subtracting on particles that are on the same level. You can produce a comparable level by making it a point to ensure that the denominator of each fraction you must work on is the same.
You will need to learn how to compute the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators of all the fractions involved, even though a fraction calculator can do this computation immediately. The least significant figure (LCM) is the lowest number that can be factored mathematically using all related denominators. Consider the most basic example of the numbers 3 and 4. Their least common multiple is 12, the lowest standard number that can be divided by both of their numbers.
One method for determining the LCM is to list the multiples of every denominator used in the computation and then select the number that is the least common multiple of those multiples. After that, you’ll be able to multiply the numerator as well as the denominator of each fraction by the appropriate factor for that denominator.
You should be able to grasp this concept with the help of a single example, in which we try to combine the fractions 2/3 and 1/4. As was discussed, the product obtained by adding the multiples of 3 and 4 is 12. In this particular instance, the factor for the first fraction is four because the sum of three times four is 12, and the factor for the second fraction is three since the sum of four times three is also 12, which is 12.
When the necessary factor is multiplied by the original fraction, the outcome is two new fractions with the values 8/12 and 3/12, respectively. When the denominators of the fractions are the same, we can quickly generate the answer 11/12 by adding the numerators of both particles and then combining that number with the common denominator. This would be the final solution.
Importance and Uses of Fractions
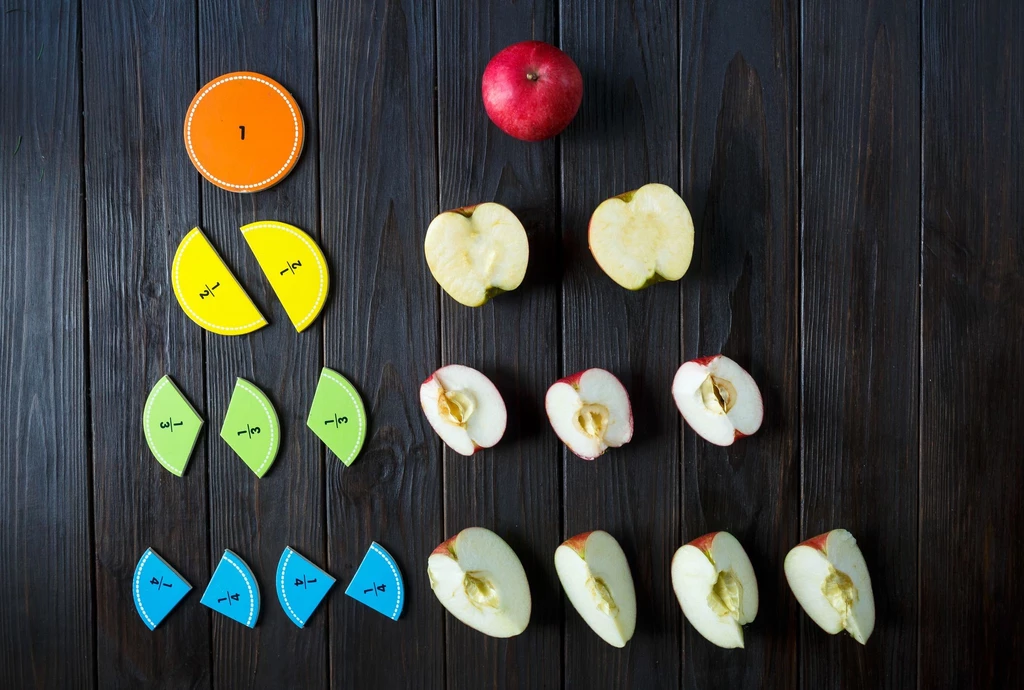
A straightforward use would be a fraction calculator to determine the answer to a question with many variables expressed as a fractional number. Nevertheless, there are many fields of endeavor and aspects of life in which fractions play a vital part, even if we do not immediately notice this fact.
In this sense, one of the essential examples is cooking, which emphasizes the need to use the appropriate fractions. If you alter the balance of just one component, you will discover that the whole meal is rendered unusable.
Another illustration of this is the process of determining the amount of a discount while shopping. The percentages are typically mentioned while talking about sales at many different shops. Using a relevant fractional calculator, you can choose how much you will save on a particular purchase.
This is significant even if a considerable percentage discount appears to be an excellent opportunity to purchase because it may give the impression that it will save a lot of money.
When it originates time to pay the taxes, you’ll need to use fractions, which illustrates their importance. Because they represent a tiny portion of your overall net income, you must accurately and thoroughly calculate all the relevant figures before making any decisions. In the circumstances like these, it’s possible that using a fraction calculator is the best action to take.
